Example: supporting GDPR
In this example, a company owns several apps that consumers use. Since the company operates in the European Union, it must comply with the GDPR regulation. Among other things, this regulation grants EU citizens the right to have companies delete their data.
The company’s apps store data about their users. On top of that, the apps use shared services that also store data about those users.
Requirements
We start by discovering the requirements. For demonstration purposes, we’ll show this process in a simplified, structured form. The analyst asks a question, the stakeholder gives an answer, and the analyst shows the resulting model.
Q: What can I do for you?
A: I want a system to support GDPR:

Q: What interesting things happen in this system?
A: Users delete their data with it:
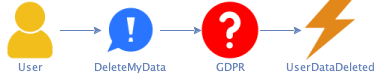
Q: How does the system know who the user is? Otherwise, it won’t know what data to delete.
A: The user either logs in to one of our apps and issues the command from there:

Or the user fills out an online form, and our customer support agents validate their identity against the apps’ user databases:
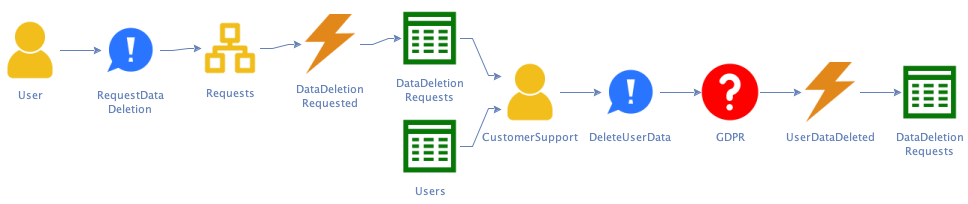
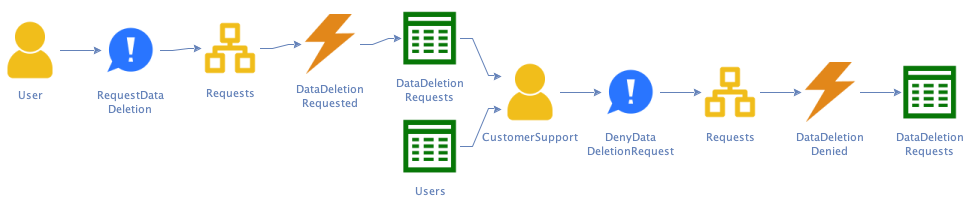
Q: What happens when the user’s request is invalid? For instance, when I use the form to request deletion of someone else’s data?
A: Customer support looks up the user via the provided email address. If there is no user with that address, we deny the request and the process ends. Otherwise, customer support contacts the user via email. If the user doesn’t respond in time, we deny the request. If the user responds they didn’t send the request, we also deny the request:
Q: How does the system know what users the apps have?
A: The app notifies the system of any changes in its users:

Q: How does the system delete the user’s data?
A: It has to tell all our services to delete the data. They’ll do the actual deletion and report back when they’re done.
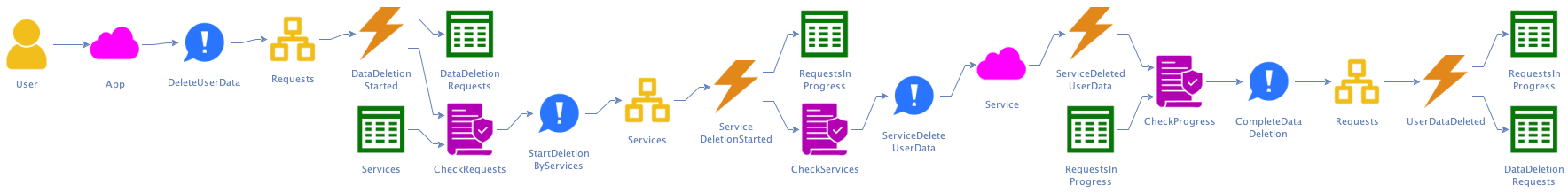
Q: What happens when a service doesn’t respond?
A: After some time, we’ll call them again.
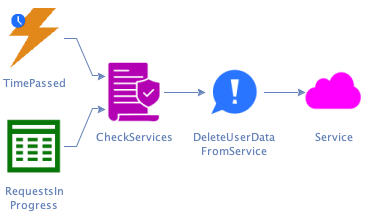
Q: What happens when all services have responded back?
A: Then the request is complete, and we inform the user.
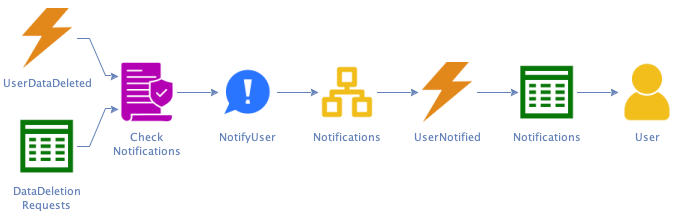
At this point, the process model is complete, since there are no more hotspots.
Note that the analyst did some initial design during the requirements elicitation process. Two situations makes this is possible:
- The model contains a sequence of command → hotspot → event where it’s clear what needs to happen in the hotspot and what information that requires. In that case, the analyst can replace the hotspot with an aggregate named after the required information.
- Similar considerations apply to a sequence of event → hotspot → command. Here, the analyst replaces the hotspot with a policy that takes input from a read model.
Just because the process model is complete, doesn’t mean we’re done with requirements gathering. We should define acceptance tests for automated policies, aggregates, and read models.
Design
The dependency graph for the above process looks like this:
graph dataDeletionRequestFormAggregate(DataDeletionRequestForm) servicesAggregate(Services) notificationsAggregate(Notifications) deletionsInProgressReadModel[[DeletionsInProgress]] dataDeletionCompletionReadModel[[DataDeletionCompletion]] checkUnresponsiveServiceAutomaticPolicy[/CheckUnresponsiveService/] checkRequestCompleteAutomaticPolicy[/CheckRequestComplete/] servicesAggregate --> checkUnresponsiveServiceAutomaticPolicy notificationsAggregate --> checkRequestCompleteAutomaticPolicy deletionsInProgressReadModel --> servicesAggregate dataDeletionCompletionReadModel --> notificationsAggregate checkUnresponsiveServiceAutomaticPolicy --> deletionsInProgressReadModel checkRequestCompleteAutomaticPolicy --> deletionsInProgressReadModel
- The graph has one cycle, so we create a module containing
Services,CheckUnresponsiveSerivces, andDeletionsInProgress. Let’s call this moduleServices, after its only aggregate. - We create two new modules for the unassigned aggregates
DataDeletionRequestFormandNotifications. - The read model
DataDeletionCompletiononly has one outgoing edge, so we assign it to theNotificationsmodule. - We assign the automatic policy
CheckRequestCompleteto the module that contains its read model,Services.
This gives us three loosely coupled modules:
graph dataDeletionRequestFormModule["<b>DataDeletionRequestForm</b> - DataDeletionRequestForm - DataDeletionRequested - DeleteMyData"] servicesModule["<b>Services</b> - CheckRequestComplete - CheckUnresponsiveService - DataDeletedInService - DataDeletionRequestedInService - DataDeletionStarted - DeleteData - DeletionsInProgress - RemindService - Services - TimePassed"] notificationsModule["<b>Notifications</b> - DataDeleted - DataDeletionCompletion - InformUser - Notifications"] servicesModule --> notificationsModule